Today, climate change is a problem that haunts planet Earth and has become the subject of study by many experts worldwide. The development of renewable energy technologies has been a fundamental pillar contributing to decarbonization, a key point in combating climate change.
In the electricity generation sector, there has been significant growth in the development of these technologies, especially in photovoltaic projects, which has generated great interest. According to the Statistical Office of the European Commission (Eurostat), in 2008 it represented 1%, 7.4 TWh, of total electricity generation at European level and in 2021 it will represent 15.1%, equivalent to 163.8 TWh. In fact, this technology in the electricity generation sector is the one that has experienced the greatest growth compared to others related to renewable energies.
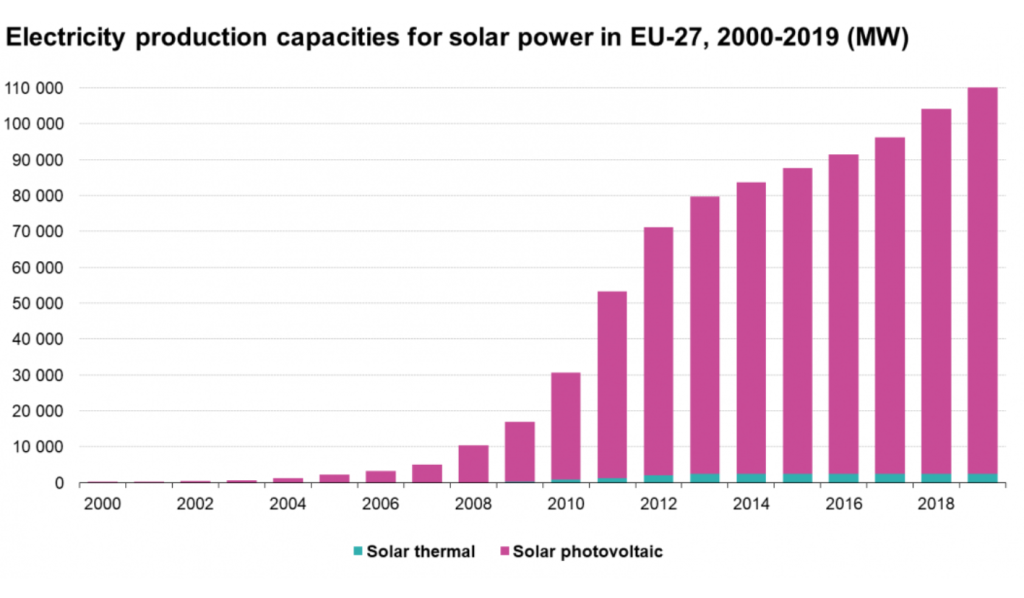
Source: Eurostat
However, this increase in PV generation projects, which has been significantly high in the electricity market, has produced a phenomenon called price cannibalization.
Price cannibalization in PV generation refers to the significant reduction in electricity market prices, which translates into a lower economic remuneration for these projects, because of the oversupply of this technology during sunshine hours.
As more photovoltaic generation projects participate in the energy mix when there is more solar radiation, conventional technologies, especially thermal ones, are being displaced, which generates an oversupply of renewable generation that exceeds demand and a considerable decrease in electricity prices, which can reach the lower limits allowed. It should also be noted that photovoltaic generation is one of the technologies with very low marginal costs due to its zero-fuel cost and low maintenance and operating costs. Therefore, this contributes to the fact that photovoltaic generation projects, it could be said that, under perfect conditions, this technology offers an almost zero marginal cost.
The above behavior can be described graphically in what is known as the “duck curve”, where as the share of PV in the energy mix increases, the price per MWh decreases.
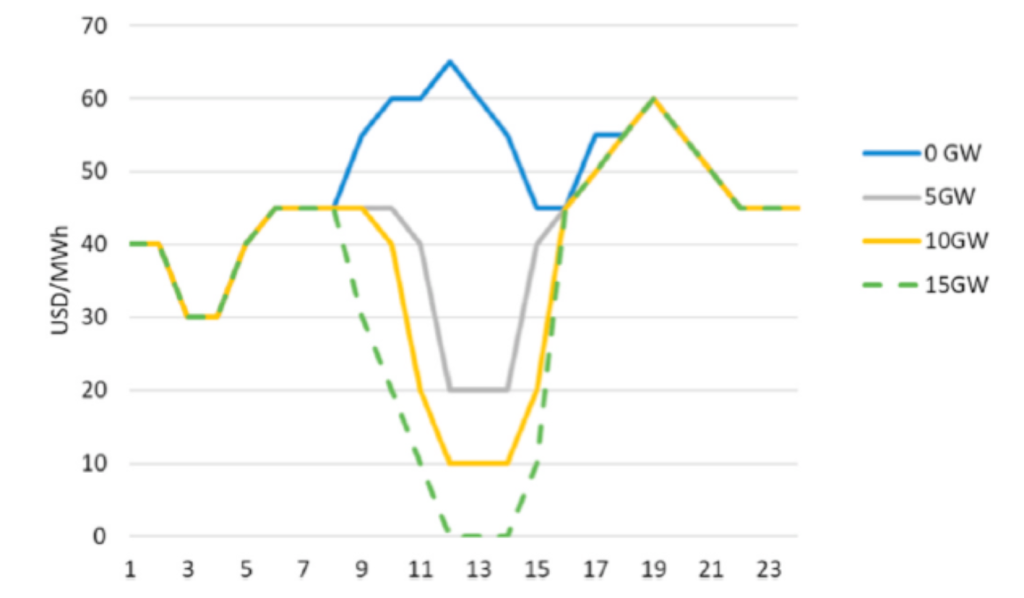
Example of a typical day of duck curve formation in photovoltaic generation. Source: Haas, R., Duic, N., Auer, H., Ajanovic, A., Ramsebner, J., Knapek, J., & Zwickl-Bernhard, S. (2023). The photovoltaic revolution is on: How it will change the electricity system in a lasting way. Energy, 265, 126351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.126351.
While it is true that this cannibalization phenomenon is quite attractive for consumers, since low or zero prices in the electricity market are beneficial in terms of costs, there are latent financial and operational risks that put the price cannibalization of photovoltaic generation in the sights of many experts in the field.
Main Problems
Uncertainty in the profitability of future projects: Price cannibalization makes it increasingly difficult to predict the medium- and long-term profitability of PV projects. This is unattractive for investors and financial institutions, which could jeopardize future economic support for this technology.
Impact on energy planning: This problem may result in difficulties in predicting the evolution of future prices of photovoltaic electricity generation, due to the uncertainty in the growth of the technology and the evolution of demand.
Impact on the planning of future projects: Cannibalization may hinder the planning of new photovoltaic generation projects, due to the uncertainty in the recovery of the initial investment considering the low market prices during sunlight hours and the current oversupply.
Reduced revenues for existing PV projects: Owners of solar plants may experience considerable reductions in their revenues, considering the low prices in the wholesale market during periods with high solar radiation. This would affect the recovery of the project’s initial investment and could possibly lead to problems with investors or financial entities.
Negative impact and volatility in conventional technologies: This phenomenon may lead to unfair competition in the wholesale market, since the low prices that occur during the hours of highest solar radiation may affect the competitiveness of other conventional generation technologies.
Instability in the electric grid: The increase in photovoltaic generation technology may generate instability in the electric grid, which may require modifications to ensure the security and stability of supply.
Although the outlook looks a bit dark economically speaking, solutions are being proposed to mitigate or eliminate the cannibalization effect of photovoltaic generation.
Possible Solutions
Incorporate energy storage systems: The implementation of energy storage processes, such as batteries, allows PV generation projects to capture excess energy during hours when there is excessive sunlight, which can be used later, either at night or when the sky is very cloudy.
Increased participation in PPAs: Long-term contracts, such as PPAs, can help provide security and stability in PV project revenues, given that prices and indexed agreements are fixed for several years.
Electricity market reforms: Create strategies in the existing electricity markets so that PV generation in the energy mix has better conditions in terms of flexibility, prices and contributes to grid stability and energy security. Although it is true that this point is one of the many that the reform of the existing markets being proposed at European level is seeking.
Policy and regulatory flexibility: Considering the intermittency of PV-based electricity production, flexibility is key. The policies and regulations of each government could adjust subsidies and incentives for these projects, reviewing the behavior of energy demand and capacity studies.
Promote integration of other technologies: In order not to have an oversupply of PV, it is fair to have a diversification considering other technologies. In addition, projects could be carried out where different technologies work together and could work in a complementary manner.
Improve demand management: Having a better management of energy demand could contribute to a balance between supply and demand, which could reduce the oversupply of photovoltaic projects in sunny hours.
According to the above, the development of photovoltaic generation and its inclusion in the electricity markets has brought several benefits, especially its contribution to reducing dependence on fossil fuels. However, the cannibalization of the prices of this technology is a black spot that we are working every day to mitigate and, if possible, eliminate, and thus provide the security that everyone needs, from generators to consumers, so that these projects can continue to help the sustainability that is so much sought after today.
Yanina Albor | Energy Consultant
References
Peña, J. Rodríguez, R. Mayoral, S (2022). Cannibalization, depredation, and market remuneration of power plants. Energy Policy 167 (26). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113086
Haas, R. Duic, N (2023). The photovoltaic revolution is on: How it will change the electricity system in a lasting way. Energy 265 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.126351
Eurostat (2021). Wind and water provide most renewable electricity; solar is the fastest-growing energy source. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Renewable_energy_statistics#Wind_and_water_provide_most_renewable_electricity.3B_solar_is_the_fastest-growing_energy_source
The weekend read: Price cannibalization threatens PV growth – pv magazine International (pv-magazine.com). https://www.pv-magazine.com/2021/10/02/the-weekend-read-price-cannibalization-threatens-pv-growth/
If you found it interesting, please share it!
Recent Articles